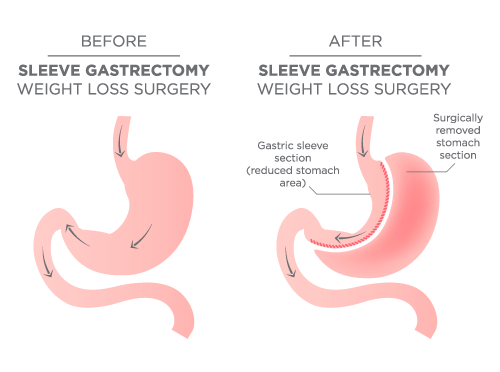
About 80% of the stomach is removed, giving the appearance of a tube or sleeve.
In the gastric sleeve procedure, the stomach is stapled along to form a thin tube that connects the esophagus to the small intestine while around 60-80% of the stomach is removed, including the portion that produce hunger-stimulating hormone. A major advantage of this procedure is that no digestive functions of the stomach are affected; only his capacity is reduced to a third. Because the size of the stomach is smaller and therefore holds less food, patients feel satisfied sooner and consequently lose weight.
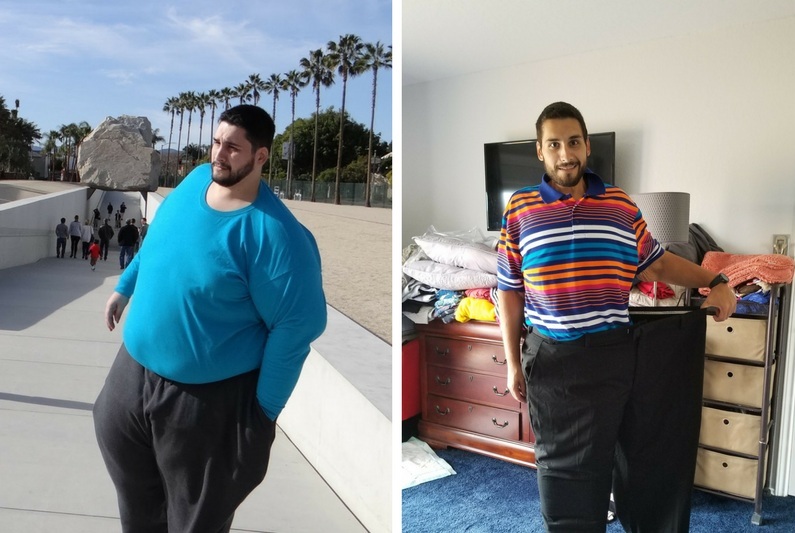
The gastric sleeve is currently used in two ways: as a single, definitive procedure, which has shown great results of up to 70% excess weight loss. Or as a ‘first step’ prior to a more complicated technique such as gastric bypass. In very obese and high-surgical-risk patients, a gastric sleeve is performed and 12-18 months later, once the patient has dropped a considerable amount of weight, a gastric bypass is performed.
EXCESS WEIGHT LOSS:
UP TO 70%.
TYPE OF PROCEDURE:
RESTRICTIVE.
PERFORMED BY LAPAROSCOPY.
NOT REVERSIBLE.
What are the ADVANTAGES?
Induces an approximate excess weight loss of up to 70% within the first 18 months, with maintenance of more than 50% (ASMBS).
Causes favorable changes in gut hormones that suppress hunger, greatly reduce appetite and improve satiety.
It does not involve any type of prosthesis, like the lap band, so there is no possibility of body rejection.
It is a restrictive procedure that does not affect the normal digestive process, unlike gastric bypass, mini gastric bypass or duodenal switch.
Patient is very independent and does not require constant doctor visits and calibrations.
Technically, it is a much simpler technique, therefore less prone to complications.
Proven improvement in any obesity related illnesses such as hypertension and diabetes type 2. Diabetes remission rates after sleeve gastrectomy are also very high, more than 60% (ASMBS).
Low possibility of malnutrition since nutrients and vitamins are fully absorbed.
Performed by laparoscopy, which means shorter recovery time, fewer and smaller incisions and less pain.
what are the POSSIBLE RISKS/CONS?
This procedure has less complications than any other type of bariatric surgery and the percentage of patients who present them is relatively small. Some of the potential risks are:
Filtration and leaking from the stomach stapling line.
Possibility of developing gastritis or stomach ulcers.
Vomiting, if the patient tends to eat more than the restricted stomach can accept.
No malabsorptive component means patients must work harder to achieve weight loss goals.
There is a possibility to stretch out the new stomach after gastric sleeve if patients do not pay attention to the amount of food ingested and portion size. The stomach will expand trying to fit the extra food and weight loss will be tampered.
To fully assess and understand all possible complications and side effects, it’s important to talk your bariatric surgeon in regards to your specific health condition.
Are you a candidate for gastric sleeve?
We believe you can be an ideal candidate for gastric sleeve if you have:
A body mass index (BMI) of 40 or more, or
At least 80 pounds (35 kg) more than your ideal weight, or
A BMI between 30 and 39.9 with a serious obesity-related health problem like diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, high cholesterol, joint problems, and many others.
You have tried, for a period of time, diverse methods (exercise, nutritional help, support groups) for the definitive weight loss without achieving successful results.
Interested in the Gastric Sleeve? Let us help!Gastric Sleeve Success Stories
*Results may vary
*Results may vary